Biotechnology terms are becoming increasingly important in our daily conversations about health, food, and the environment. Biotechnology is a fascinating science that uses living organisms, such as bacteria, cells, or even parts of them, to create products and solutions that make our lives better. Thanks to biotechnology, today we can produce life-saving medicines, develop safer and more nutritious food, protect the environment, and prevent many diseases that once seemed impossible to stop.
What makes biotechnology even more exciting is how it turns slow and complex processes into faster, more efficient ones. For example, producing certain medicines used to take years of manual work, and now, thanks to biotechnology, they can be made in modern laboratories in a matter of days. This same science allows plants to grow stronger and more resistant, helps clean contaminated water, and is even behind some of the vaccines that protect us from dangerous viruses.
Biotechnology is not only present in big scientific laboratories or hospitals. It plays a key role in many aspects of our everyday lives, often without us realizing it. When we eat yogurt, enjoy a slice of cheese, take a vaccine, or see crops that grow healthier and faster, biotechnology is working behind the scenes.
To help you better understand biotechnology terms, this illustrated glossary presents 20 essential words commonly used in this field. Each word is explained in a clear and simple way, perfect for young students, curious minds, or anyone who wants to learn more about the exciting world of biotechnology.
Glossary of key biotechnology terms
The smallest unit of a living being. All living beings are made of cells. Some are simple, like bacteria, and others very complex, like human cells.
A very small living being that can only be seen through a microscope. Some bacteria help our bodies, such as those in the intestines, while others can cause diseases. They are found in many places: in the air, water, food, and our bodies.
A microscopic agent that needs to enter a cell to reproduce. It is not a complete living being and can cause diseases like the flu or COVID-19.

Cell

Bacterium
Virus
What is a DNA?
The material that holds the genetic information of all living beings. It is inside the nucleus of our cells and works like an instruction manual that tells how our body forms and functions.
Similar to DNA, but works as a messenger. It copies the information from DNA and carries it to other parts of the cell to help make proteins.
What is a gene?
A fragment of DNA that contains the information to make a protein or control a body function. Genes are like small instructions that determine traits such as eye color or how a cell works. We all have thousands of genes, which together form our genetic material.

DNA

RNA
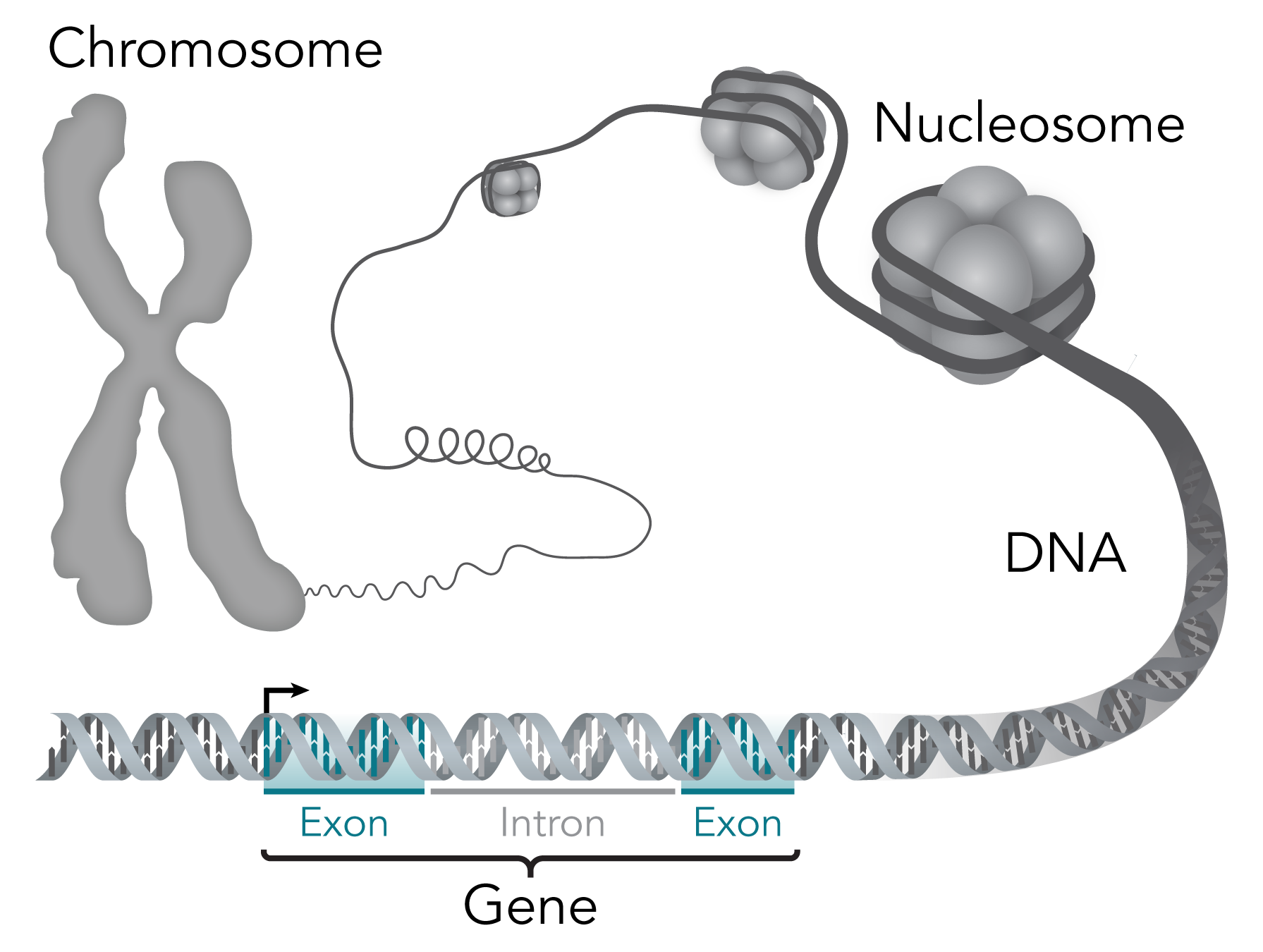
Gene
A set of techniques that allow changing the DNA of a living being to improve it or give it new functions. It is used to make more resistant plants, produce medicines, etc.
What is Genetically Modified Organism (GMO)?
A living being, like a plant or bacterium, whose DNA has been changed to give it some advantage, such as growing faster or resisting diseases better.
A very precise technique that allows editing parts of DNA like scissors. It is used to correct genetic errors or study genetic diseases.

Genetic engineering

Genetically modified organism
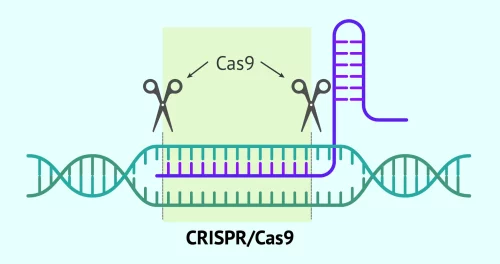
CRISPR
What is cell culture?
A technique that allows cells to grow in a laboratory. They are placed in a container with nutrients and cared for to keep them alive and reproducing. It is used to study diseases or make vaccines.
What is Fermentation?
A process in which microorganisms transform substances like sugar into other products, such as alcohol or yogurt. It is widely used in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
what is a bioreactor?
A machine that allows microorganisms or cells to grow under very controlled conditions. It is used to produce medicines, food, and other useful products.

Cell culture

Fermentation

Bioreactor
What are enzymes?
Proteins that make chemical reactions in the body happen faster. For example, they help digest food. They are also used in products like detergents and juices.
What are recombinant proteins?
A protein made in a laboratory with the help of microorganisms, such as insulin used to treat diabetes.
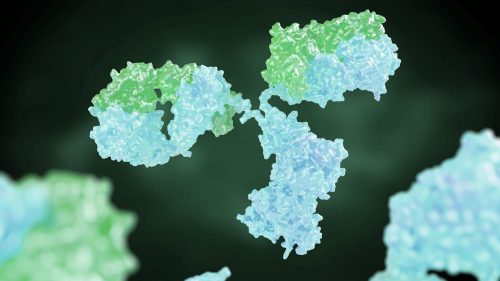
What are antibodies?
A protein made by the body to defend against viruses or bacteria. They can also be made in a lab to help cure diseases.
Enzymes
Recombinant protein
Antibody
What is molecular diagnostics?
A method to detect diseases by analyzing the DNA or RNA of a person or virus. It is very useful to find out if someone has an infection or a genetic disease.
A treatment that tries to cure diseases by changing the genes inside cells. For example, it is used to treat hereditary diseases.
What is cloning?
Making an exact copy of a living being or a cell. It can be used for research, treating diseases, or conserving endangered animals.
What is the microbiome?
The set of microbes (like bacteria) that live in our bodies, especially in the intestines. They are very important for digestion and health.
What are vaccines?
A product introduced into the body to teach the immune system to defend against viruses or bacteria. Many vaccines are made with the help of biotechnology.

Gene editing

Microbiome
Vaccine
Conclusion
Understanding biotechnology terms is the first step to discovering how this incredible science shapes our world. By learning these essential terms, we open the door to understanding how medicines, vaccines, and everyday products are created using living organisms.
These biotechnology terms help us see the invisible work of scientists who use cells, bacteria, and other microorganisms to improve health, food, and environmental care. They also allow us to recognize the role of biotechnology in making our lives easier, safer, and healthier.
Even if you are not a scientist, knowing basic biotechnology terms can help you better understand the news, school topics, or even conversations about health and food safety. It makes us more informed citizens and shows us how biology and technology come together to create solutions for the challenges of today and tomorrow.
In this glossary, you have learned 20 of the most important biotechnology terms, explained in a simple and friendly way, so that anyone—whether a student, a teacher, or simply a curious person—can understand the basics of biotechnology.
Remember, these biotechnology terms are not just scientific words; they represent the tools and ideas that will continue to change the world around us.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
It is the science that uses living organisms to create useful products, like medicines or vaccines.
A bacterium is a living cell; a virus is a particle that needs a cell to reproduce.
To transform substances like sugar into useful products, such as yogurt or alcohol.
No. Many bacteria are helpful, for example, those that live in the intestines and help digest food.
Because it helps us improve health, food, the environment, and create better medicines.